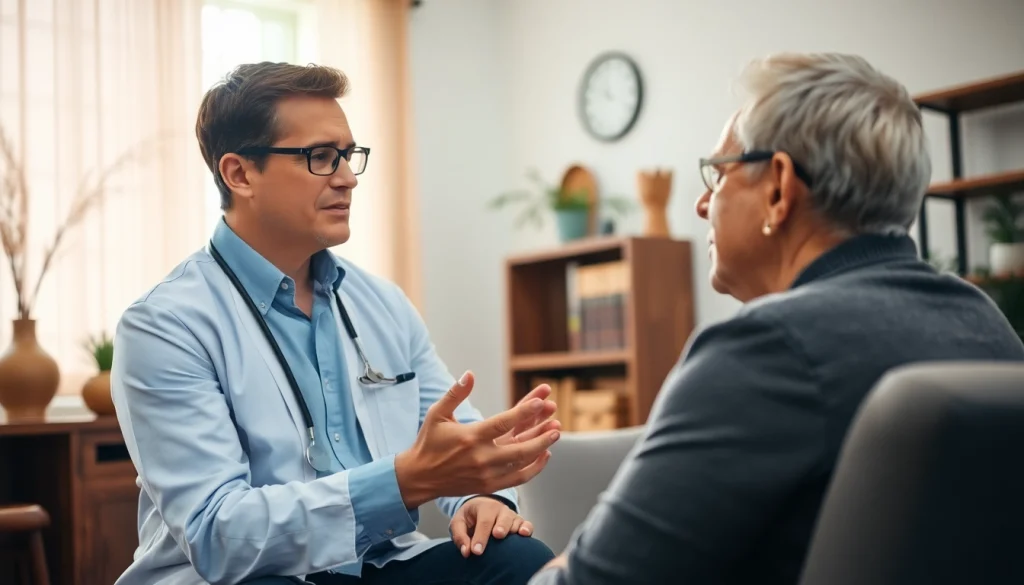
What Are Anxiety Symptoms?
Defining Anxiety Symptoms
Anxiety symptoms encompass a range of physical, cognitive, and emotional responses that arise in reaction to perceived threats or stressors. Individuals experiencing anxiety often report feelings of unease, fear, or dread, often accompanied by physiological changes such as increased heart rate or sweating. By understanding anxiety symptoms, we can better recognize their impact on our well-being and daily functioning.
Common Types of Anxiety Symptoms
Anxiety symptoms can be classified into several categories, including:
- Physical Symptoms: These may include rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, fatigue, and difficulty sleeping.
- Cognitive Symptoms: Individuals may experience racing thoughts, difficulty concentrating, and an overwhelming sense of impending doom.
- Emotional Symptoms: Feelings of panic, fear, irritability, and a sense of detachment can pervade daily life.
The Impact of Anxiety Symptoms on Daily Life
The effects of anxiety symptoms go beyond individual experiences; they influence relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life. For instance, constant worry may lead to avoidance behavior, which can hinder social interactions and career advancement. Understanding how anxiety symptoms manifest in daily situations is crucial for effective management and support.
Recognizing Anxiety Symptoms
Physical Manifestations of Anxiety Symptoms
Physical manifestations of anxiety symptoms can vary widely among individuals. Common traits include muscle tension, headaches, gastrointestinal disturbances, and changes in appetite. Recognizing these signs can be critical for early intervention, potentially preventing symptoms from escalating.
Cognitive Effects of Anxiety Symptoms
Cognitive effects associated with anxiety symptoms commonly involve a constant stream of anxious thoughts. Sufferers may find themselves trapped in cycles of negative thinking or may struggle to focus on tasks. This cognitive struggle not only affects personal well-being but could also have educational or occupational ramifications.
Emotional Indicators of Anxiety Symptoms
Emotional indicators of anxiety can include pervasive feelings of hopelessness, irritability, or guilt. Individuals may also experience sudden episodes of distress or panic that seem to arise out of nowhere. Awareness of these emotional signals is paramount in tackling anxiety effectively.
Causes of Anxiety Symptoms
Biological Factors Leading to Anxiety Symptoms
Anxiety symptoms can be attributed to a combination of genetic, neurological, and hormonal factors. For instance, imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine play significant roles in anxiety. Additionally, a family history of anxiety disorders may predispose individuals to similar challenges, leading to greater sensitivity to stressors.
Environmental Triggers for Anxiety Symptoms
Environmental factors such as trauma, chronic stress, and significant life changes can precipitate anxiety symptoms. Varied triggers can range from losing a loved one to facing job insecurity. Identifying these external elements can provide insights into personal coping strategies and preventative measures.
Psychological Influences on Anxiety Symptoms
Psychological influences, including personality traits and learned behaviors, contribute heavily to anxiety symptoms. For instance, perfectionists or those with high levels of neuroticism may be more susceptible to anxiety. Cognitive distortions, such as catastrophizing or black-and-white thinking, can also perpetuate anxiety, necessitating awareness and cognitive reframing.
Managing Anxiety Symptoms
Effective Coping Strategies for Anxiety Symptoms
Diverse coping strategies can help manage anxiety symptoms effectively. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, controlled breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can provide immediate relief during anxious moments. Other methods include engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and establishing strong social support networks.
When to Seek Professional Help for Anxiety Symptoms
It is crucial to seek professional help when anxiety symptoms begin to interfere significantly with daily life. Symptoms that lead to avoidance behaviors, disrupt interpersonal relationships, or affect job performance warrant consultation with a mental health professional. Early intervention can facilitate effective treatment and support.
Long-term Approaches to Address Anxiety Symptoms
Long-term management of anxiety symptoms may involve a combination of therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) has proven effective in changing negative thought patterns associated with anxiety. Furthermore, some may find that medications such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs provide necessary support during critical periods.
FAQs About Anxiety Symptoms
What are the early signs of anxiety symptoms?
Early signs include increased heart rate, restlessness, and excessive worrying. Recognizing these early indicators can lead to more effective management strategies.
How can I differentiate anxiety symptoms from stress?
Anxiety symptoms persist longer and can occur without identifiable stressors, unlike typical stress reactions triggered by specific events. Understanding this difference is vital for treatment.
Are anxiety symptoms treatable?
Yes, various therapies and medications can effectively treat anxiety symptoms. A combination of approaches often yields the best results.
When should I see a doctor about anxiety symptoms?
Consult a doctor if symptoms interfere with daily life or cause significant distress, helping to determine the best course of action.
Do anxiety symptoms always require medication?
No, many people manage anxiety symptoms with therapy, lifestyle changes, and coping strategies that may reduce their severity effectively.